TL;DR
- Email validation checks whether an email address could exist based on format, syntax, and basic rules.
- Email verification confirms whether the mailbox actually exists and can receive emails using technical checks (MX, SMTP, accept-all detection).
- An email checker (or email verifier) is a tool that combines both validation and verification.
- Validation alone catches typos and obvious errors but doesn’t prevent hard bounces.
- Verification goes deeper and is what truly protects sender reputation and deliverability.
- Accept-all domains and disposable emails add risk and teach why verification matters beyond format checks.
- Relying only on validation leads to higher bounce rates and inbox placement issues.
- Bottom line: validation checks structure, verification checks reality—and the best email checkers do both.
You might have heard the terms “email validation,” “email verification,” and “email checker” used interchangeably. Or you might have gotten them confused while planning your own cold outreach strategy.
Each describes a different part of the same process: ensuring your emails reach the inbox. After all, accurate email addresses are the foundation of effective outreach.
Although these terms are related, mistaking one for the others could cost you in terms of email deliverability. Each is an essential part of maintaining a healthy email list and protecting your sender reputation.
In this article, I’ll clarify the difference so you know which tool or process you need for email outreach. I’ll also walk you through how Hunter’s Email Verifier helps you with all three.
Quick Summary: The Difference in 60 Seconds
- Email validation is the process of checking the syntax and formatting of an email address
- Email verification is a process that validates email address structure and confirms that the mailbox exists and can receive emails
- Email checker (also known as email verifier) is a tool that performs both validation and verification to maximize email deliverability
What is email validation?
Email validation confirms whether an email address could exist based on factors like its format and domain.
Hunter’s Email Verifier uses the following checks to validate email addresses:
Format and syntax
All valid email addresses follow a few standard formatting and syntax rules. Every address should contain a username, an “@” symbol, and a domain (e.g., “.com” or “.io”).
The Email Verifier checks to make sure the email address doesn’t contain multiple “@” symbols, any spaces, or invalid characters like periods at the beginning or end of the username.
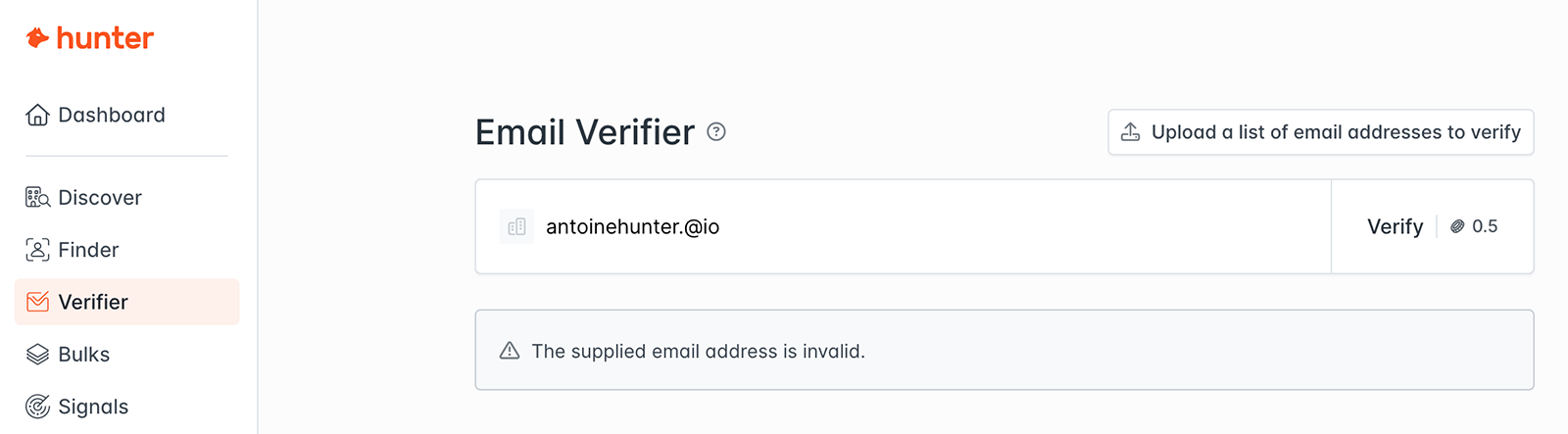
For example:
- ✅ email@provider.com follows the correct format
- ❌ emailprovider.@com doesn’t have a valid domain
- ❌ e mail@provider.com has a space in the username
Random usernames
Email addresses can include a range of characters—including letters, numbers, and certain symbols. But valid email usernames shouldn’t include a random mix of characters.
The Email Verifier checks for random character strings in the local part of the email (the username) and flags them if they don’t look like human words, names, or patterns.
For example, an email address with random characters like 1e49cs1pb6@provider.com wouldn’t pass the gibberish detector.
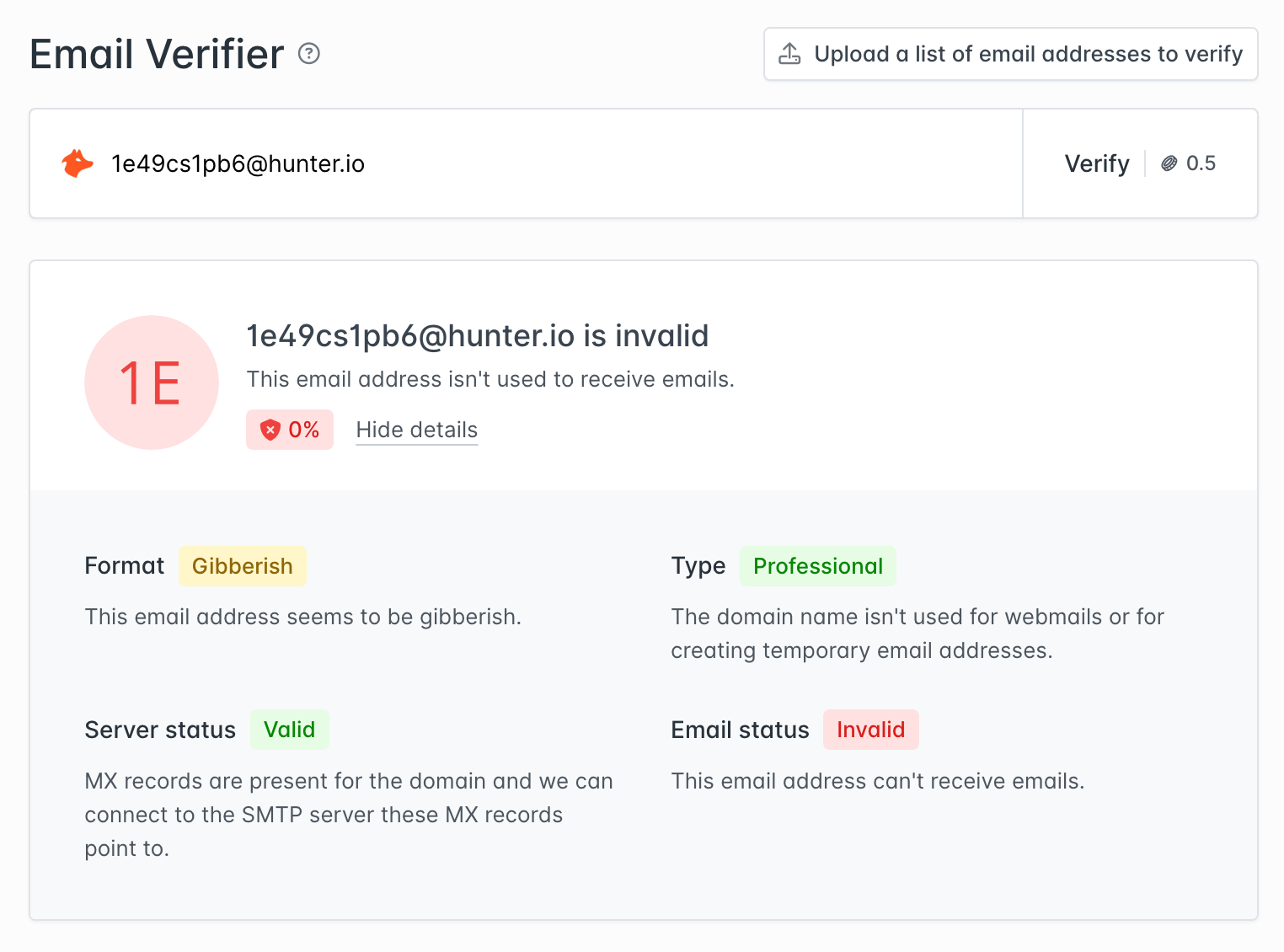
Disposable email addresses
A disposable email address is designed to be temporary, typically for a single use like signing up for a one-time service. That means it isn’t a valid address for outreach.
To catch these email addresses, Hunter checks for disposable and other risky email domains like Guerrilla Mail, TempMail, Maildrop, Mailinator, and many others.
Webmail email addresses
Generally, email addresses with professional domains (like employee@company.com) are considered more reputable and trustworthy than those with webmail domains.
But webmail services like Gmail and Yahoo are considered mainstream. This means their trust signal is relatively high.
The Email Verifier confirms if an email address uses a webmail service. That way, if your outreach campaign prioritizes professional email addresses, you can easily remove contacts with webmail email addresses.
What is email verification?
Email verification confirms whether the mailbox actually exists and can receive messages. This is where the real deliverability assurance happens.
The verification process goes beyond validation to check technical aspects like mail exchange (MX) records and simple mail transfer protocol (SMTP) servers.
Hunter’s Email Verifier uses these checks to verify email addresses:
MX records
An MX record points to the mail server that receives emails for a domain. If there are no MX records, the domain can’t receive emails.
This means any email address tied to the domain is invalid—and any email you send to the domain can’t be delivered. As a result, MX records are one of the first elements Hunter checks.
SMTP servers
SMTP servers send and receive emails. Without an SMTP server, the domain can’t receive emails—which means any emails you send to the address would bounce.
To confirm the presence of the SMTP server, The Email Verifier connects to the server reflected in the MX record for the domain.
SMTP checks
An SMTP check tests the email address to confirm that it exists. If the SMTP server prevents the Email Verifier from completing this check, it marks the email address as “Blocked.”
Accept-all domains
Accept-all domains have a policy that receives all incoming emails, even if the specific mailbox doesn’t exist. Hunter checks for these catch-all policies because email addresses marked as “Accept-All” still have the potential to bounce—which negatively impacts deliverability.
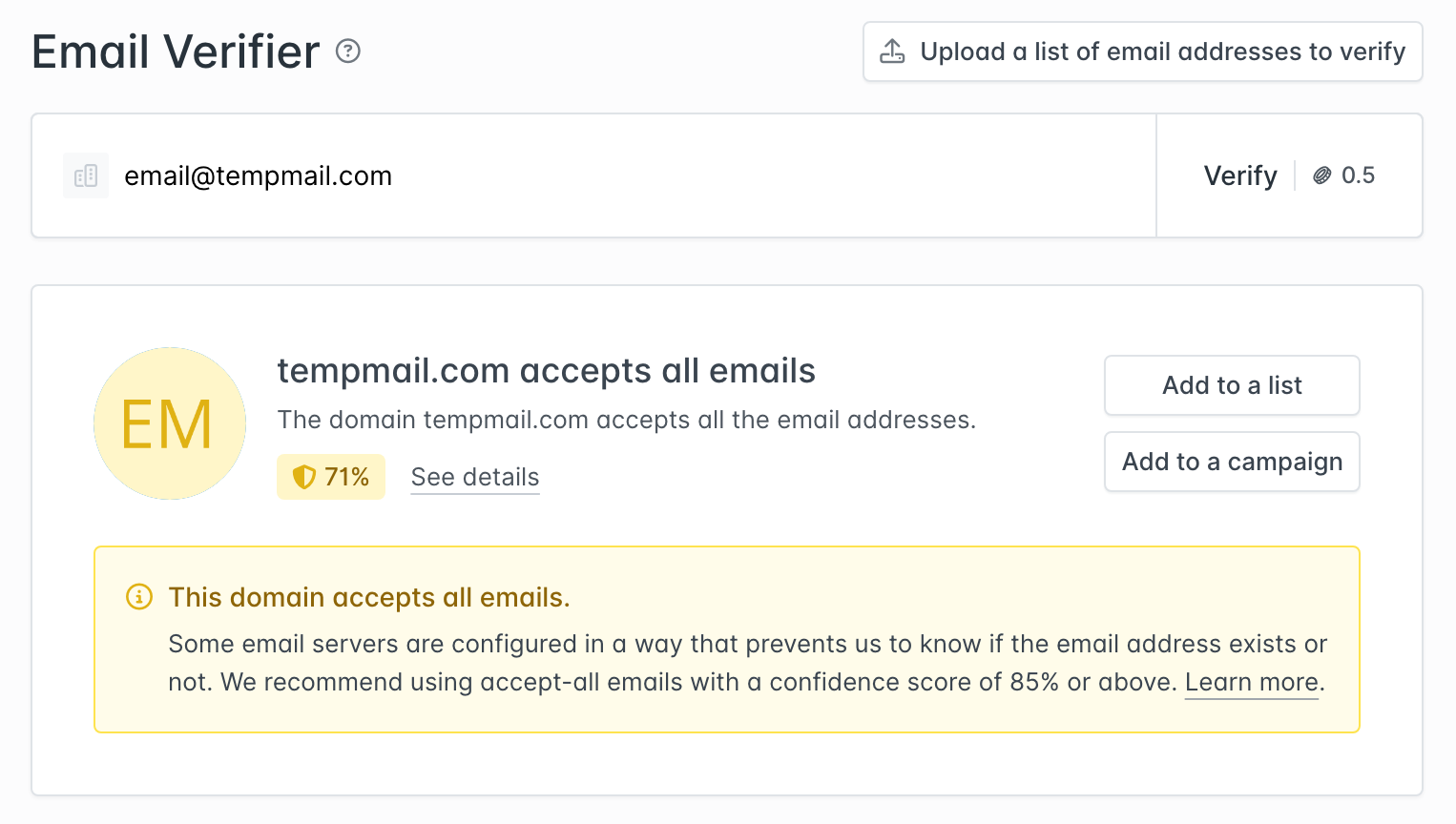
What about email checkers?
An email checker is another word for email verifier. Don’t let that terminology confuse you, though. Most email checkers handle both validation and verification.
Hunter’s Email Verifier is an email checker that goes the extra mile in terms of accuracy and up-to-date infrastructure.
Instead of relying on publicly available data, it performs technical checks to verify MX records and SMTP servers. This reduces your bounce rate and improves your deliverability.
Why the distinction between email validation vs. email verification matters
If you depend solely on email validation, you might catch some typos. But this process alone won’t prevent hard bounces.
Email verification is a more thorough process that produces more accurate results. It’s designed to protect sender reputation and lower bounce rate—leading to higher ROI from email marketing and cold email.
Outdated and incomplete checks can cause serious damage. Unverified email data can cost you in terms of higher bounce rates, spam flags, and deliverability drops.
That’s why email verification is essential for creating a reliable list of email contacts for cold outreach.
Next steps to get started with email verification
In short, validation confirms that an email address can exist given its format and syntax. Verification confirms that an email address does exist based on technical checks.
“Email checker” is synonymous with “email verifier.” And the best email checkers do both validation and verification—like Hunter’s Email Verifier.Start verifying your email list and improving your deliverability today. Test Hunter’s Email Verifier for free.
